![图片[1]-代码更新不停机:SpringBoot应用实现零停机更新的新质生产力-明恒博客](https://www.zym88.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/frc-8048571e89e0122e57202156fb8a247b.jpeg)
在个人或者企业服务器上,总归有要更新代码的时候,普通的做法必须先终止原来进程,因为新进程和老进程端口是一个,新进程在启动时候,必定会出现端口占用的情况,但是,还有黑科技可以让两个SpringBoot进程真正的共用同一个端口,这是另一种解决办法,我们下回分解。
那么就会出现一个问题,如果此时有大量的用户在访问,但是你的代码又必须要更新,这时候如果采用上面的做法,那么必定会导致一段时间内的用户无法访问,这段时间还取决于你的项目启动速度,那么在单体应用下,如何解决这种事情?
一种简单办法是,新代码先用其他端口启动,启动完毕后,更改nginx的转发地址,nginx重启非常快,这样就避免了大量的用户访问失败,最后终止老进程就可以。
但是还是比较麻烦,端口换来换去,即使你写个脚本,也是比较麻烦,有没有一种可能,新进程直接启动,自动处理好这些事情?
答案是有的。
设计思路
这里涉及到几处源码类的知识,如下。
-
SpringBoot内嵌Servlet容器的原理是什么 -
DispatcherServlet是如何传递给Servlet容器的
先看第一个问题,用Tomcat来说,这个首先得Tomcat本身支持,如果Tomcat不支持内嵌,SpringBoot估计也没办法,或者可能会另找出路。
Tomcat本身有一个Tomcat类,没错就叫Tomcat,全路径是org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat,我们想启动一个Tomcat,直接new Tomcat(),之后调用start()就可以了。
并且他提供了添加Servlet、配置连接器这些基本操作。
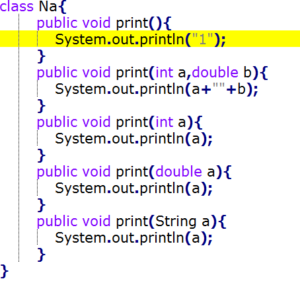
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {try {Tomcat tomcat =new Tomcat();tomcat.getConnector();tomcat.getHost();Context context = tomcat.addContext("/", null);tomcat.addServlet("/","index",new HttpServlet(){@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {resp.getWriter().append("hello");}});context.addServletMappingDecoded("/","index");tomcat.init();tomcat.start();}catch (Exception e){}}}public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Tomcat tomcat =new Tomcat(); tomcat.getConnector(); tomcat.getHost(); Context context = tomcat.addContext("/", null); tomcat.addServlet("/","index",new HttpServlet(){ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { resp.getWriter().append("hello"); } }); context.addServletMappingDecoded("/","index"); tomcat.init(); tomcat.start(); }catch (Exception e){} } }public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Tomcat tomcat =new Tomcat(); tomcat.getConnector(); tomcat.getHost(); Context context = tomcat.addContext("/", null); tomcat.addServlet("/","index",new HttpServlet(){ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { resp.getWriter().append("hello"); } }); context.addServletMappingDecoded("/","index"); tomcat.init(); tomcat.start(); }catch (Exception e){} } }
在SpringBoot源码中,根据你引入的Servlet容器依赖,通过下面代码可以获取创建对应容器的工厂,拿Tomcat来说,创建Tomcat容器的工厂类是TomcatServletWebServerFactory。
private static ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {String[] beanNames = context.getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);return context.getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);}private static ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { String[] beanNames = context.getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class); return context.getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class); }private static ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { String[] beanNames = context.getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class); return context.getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class); }
调用ServletWebServerFactory.getWebServer就可以获取一个Web服务,他有start、stop方法启动、关闭Web服务。
而getWebServer方法的参数很关键,也是第二个问题,DispatcherServlet是如何传递给Servlet容器的。
SpringBoot并不像上面Tomcat的例子一样简单的通过tomcat.addServlet把DispatcherServlet传递给Tomcat,而是通过个Tomcat主动回调来完成的,具体的回调通过ServletContainerInitializer接口协议,它允许我们动态地配置Servlet、过滤器。
SpringBoot在创建Tomcat后,会向Tomcat添加一个此接口的实现,类名是TomcatStarter,但是TomcatStarter也只是一堆SpringBoot内部ServletContextInitializer的集合,简单的封装了一下,这些集合中有一个类会向Tomcat添加DispatcherServlet
在Tomcat内部启动后,会通过此接口回调到SpringBoot内部,SpringBoot在内部会调用所有ServletContextInitializer集合来初始化,
而getWebServer的参数正好就是一堆ServletContextInitializer集合。
那么这时候还有一个问题,怎么获取ServletContextInitializer集合?
非常简单,注意,ServletContextInitializerBeans是实现Collection的。
protected static Collection getServletContextInitializerBeans(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(context.getBeanFactory());}protected static Collection getServletContextInitializerBeans(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(context.getBeanFactory()); }protected static Collection getServletContextInitializerBeans(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(context.getBeanFactory()); }
到这里所有用到的都准备完毕了,思路也很简单。
-
判断端口是否占用 -
占用则先通过其他端口启动 -
等待启动完毕后终止老进程 -
重新创建容器实例并且关联DispatcherServlet
在第三步和第四步之间,速度很快的,这样就达到了无缝更新代码的目的。
实现代码
@SpringBootApplication()@EnableSchedulingpublic class WebMainApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {String[] newArgs = args.clone();int defaultPort = 8088;boolean needChangePort = false;if (isPortInUse(defaultPort)) {newArgs = new String[args.length + 1];System.arraycopy(args, 0, newArgs, 0, args.length);newArgs[newArgs.length - 1] = "--server.port=9090";needChangePort = true;}ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(WebMainApplication.class, newArgs);if (needChangePort) {String command = String.format("lsof -i :%d | grep LISTEN | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9", defaultPort);try {Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"sh", "-c", command}).waitFor();while (isPortInUse(defaultPort)) {}ServletWebServerFactory webServerFactory = getWebServerFactory(run);((TomcatServletWebServerFactory) webServerFactory).setPort(defaultPort);WebServer webServer = webServerFactory.getWebServer(invokeSelfInitialize(((ServletWebServerApplicationContext) run)));webServer.start();((ServletWebServerApplicationContext) run).getWebServer().stop();} catch (IOException | InterruptedException ignored) {}}}private static ServletContextInitializer invokeSelfInitialize(ServletWebServerApplicationContext context) {try {Method method = ServletWebServerApplicationContext.class.getDeclaredMethod("getSelfInitializer");method.setAccessible(true);return (ServletContextInitializer) method.invoke(context);} catch (Throwable e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}private static boolean isPortInUse(int port) {try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port)) {return false;} catch (IOException e) {return true;}}protected static Collection getServletContextInitializerBeans(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(context.getBeanFactory());}private static ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {String[] beanNames = context.getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);return context.getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);}}@SpringBootApplication() @EnableScheduling public class WebMainApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] newArgs = args.clone(); int defaultPort = 8088; boolean needChangePort = false; if (isPortInUse(defaultPort)) { newArgs = new String[args.length + 1]; System.arraycopy(args, 0, newArgs, 0, args.length); newArgs[newArgs.length - 1] = "--server.port=9090"; needChangePort = true; } ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(WebMainApplication.class, newArgs); if (needChangePort) { String command = String.format("lsof -i :%d | grep LISTEN | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9", defaultPort); try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"sh", "-c", command}).waitFor(); while (isPortInUse(defaultPort)) { } ServletWebServerFactory webServerFactory = getWebServerFactory(run); ((TomcatServletWebServerFactory) webServerFactory).setPort(defaultPort); WebServer webServer = webServerFactory.getWebServer(invokeSelfInitialize(((ServletWebServerApplicationContext) run))); webServer.start(); ((ServletWebServerApplicationContext) run).getWebServer().stop(); } catch (IOException | InterruptedException ignored) { } } } private static ServletContextInitializer invokeSelfInitialize(ServletWebServerApplicationContext context) { try { Method method = ServletWebServerApplicationContext.class.getDeclaredMethod("getSelfInitializer"); method.setAccessible(true); return (ServletContextInitializer) method.invoke(context); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } private static boolean isPortInUse(int port) { try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port)) { return false; } catch (IOException e) { return true; } } protected static Collection getServletContextInitializerBeans(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(context.getBeanFactory()); } private static ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { String[] beanNames = context.getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class); return context.getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class); } }@SpringBootApplication() @EnableScheduling public class WebMainApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] newArgs = args.clone(); int defaultPort = 8088; boolean needChangePort = false; if (isPortInUse(defaultPort)) { newArgs = new String[args.length + 1]; System.arraycopy(args, 0, newArgs, 0, args.length); newArgs[newArgs.length - 1] = "--server.port=9090"; needChangePort = true; } ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(WebMainApplication.class, newArgs); if (needChangePort) { String command = String.format("lsof -i :%d | grep LISTEN | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9", defaultPort); try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"sh", "-c", command}).waitFor(); while (isPortInUse(defaultPort)) { } ServletWebServerFactory webServerFactory = getWebServerFactory(run); ((TomcatServletWebServerFactory) webServerFactory).setPort(defaultPort); WebServer webServer = webServerFactory.getWebServer(invokeSelfInitialize(((ServletWebServerApplicationContext) run))); webServer.start(); ((ServletWebServerApplicationContext) run).getWebServer().stop(); } catch (IOException | InterruptedException ignored) { } } } private static ServletContextInitializer invokeSelfInitialize(ServletWebServerApplicationContext context) { try { Method method = ServletWebServerApplicationContext.class.getDeclaredMethod("getSelfInitializer"); method.setAccessible(true); return (ServletContextInitializer) method.invoke(context); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } private static boolean isPortInUse(int port) { try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port)) { return false; } catch (IOException e) { return true; } } protected static Collection getServletContextInitializerBeans(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(context.getBeanFactory()); } private static ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { String[] beanNames = context.getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class); return context.getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class); } }
测试
我们先写一个小demo。
@RestController()@RequestMapping("port/test")public class TestPortController {@GetMapping("test")public String test() {return "1";}}@RestController() @RequestMapping("port/test") public class TestPortController { @GetMapping("test") public String test() { return "1"; } }@RestController() @RequestMapping("port/test") public class TestPortController { @GetMapping("test") public String test() { return "1"; } }
并且打包成jar,然后更改返回值为2,并打包成v2版本的jar包,此时有两个代码,一个新的一个旧的。
![图片[2]-代码更新不停机:SpringBoot应用实现零停机更新的新质生产力-明恒博客](https://www.zym88.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/frc-237b5bc6e2f2da1309aec9b10129a0e1.jpg)
我们先启动v1版本,并且使用IDEA中最好用的接口调试插件Cool Request测试,可以发现此时都正常。![图片[3]-代码更新不停机:SpringBoot应用实现零停机更新的新质生产力-明恒博客](https://www.zym88.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/frc-e19703f2aa2297fb6881c628702f2fb6.jpg)
好的我们不用关闭v1的进程,直接启动v2的jar包,并且启动后,可以一直在Cool Request测试接口时间内的可用程度。
稍等后,就会看到v2代码已经生效,而在这个过程中,服务只有极短的时间不可用,不会超过1秒。
![图片[4]-代码更新不停机:SpringBoot应用实现零停机更新的新质生产力-明恒博客](https://www.zym88.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/frc-a73a8c6dd9ae3f6df87928f0bf2343d4.jpg)
妙不妙?
4 本站一切资源不代表本站立场,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责。
5 本站一律禁止以任何方式发布或转载任何违法的相关信息,访客发现请向站长举报。
6 本站资源大多存储在云盘,如发现链接失效,请联系我们我们会第一时间更新。








![[开源] 多端适配社交圈子论坛 star 3k-明恒博客](https://www.zym88.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/640-26-300x139.png)







暂无评论内容